【Mapping】
mapping 在 Solidity 的運作就像是 python 的 dict 或常見的資料結構 hash-map。
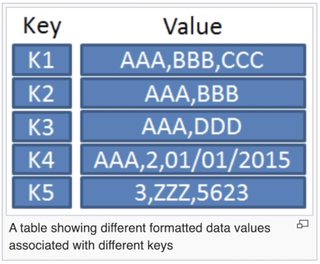
在圖中的例子,當我們 call "k1" 的時候,這個 mapping 就會回傳 key "k1" 指向的值,也就是 "AAA,BBB,CCC"。此外,我們還可以儲存新的資料進去 mapping。
mapping(uint => string) public names;在以上這段語法中,每一個 key 在這個名為 names 的 mapping 中,是以 uint 形態存在。而相對應的每個 value 型態為 string。
宣告語法為:mapping(_keyType => _valueType) name;
_keyType可以是任何的元素型態,也就是說它可以為任何的既有數值型態包含bytes和string_valueType可以是任何的型態,包含複雜的資料結構,甚至是mapping
Mapping具有以下的特色:
所有元素都會被初始化
不存在長度,如果需要紀錄長度得額外宣告一個變數
mapping的Public state variables 會成為Getter Function如果需要可遍歷的
mapping可以藉由導入一些libraries達到。
如同二維陣列,我們也可以宣告 Nested mapping 來做為類似的用途:
那既然用途很像,我們什麼時候用 array,什麼時候用 mapping 呢?我會用使用情況來區分我們要使用哪種資料結構:
當常常需要遍歷(iterate)這個資料結構時,我就會使用
array如果我們需要常常查看某些特定的鍵值(key)時,我會使用
mapping
需要注意的是,我們沒辦法使用動態記憶體配置來宣告 mapping。
Last updated